Arrays
Searching
When working with arrays, it is often necessary to perform a search or "lookup" to determine whether an array contains a value that matches a certain key value. For example, the data from a file or database table will typically contain a "key" field (such as a code), along with corresponding data fields (such as a description). It is often convenient to work with such data by first loading it into a structure array in an initial routine, and then later pulling data from the array given a key value to search on.
Three versions of a sample project to look up a state abbreviation and return the corresponding state name will now be presented. The first version demonstrates how to perform a serial search (also called a linear search) on an array; the second and third demonstrate how to perform a binary search.
These projects will process a sequential file of state abbreviations and corresponding state names called STATES.DAT, with the following contents:
"AK","ALASKA"
"AL","ALABAMA"
.
.
.
"WV","WEST VIRGINIA"
"WY","WYOMING"
Serial Search Example
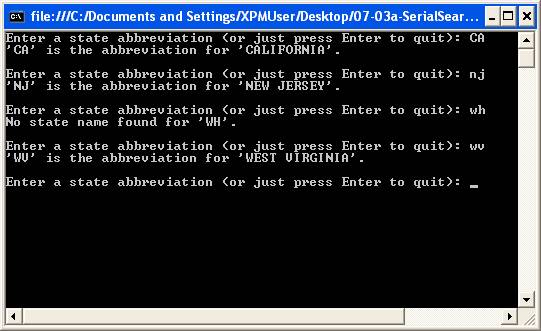
The program code and corresponding output is shown below:
|
VB Code: |
Screen-shot of run: |
|
Module Module1
Private Structure StateRecord Dim StateAbbrev As String Dim StateName As String End Structure
Private maudtStateRecord() As StateRecord
Public Sub Main()
Dim strTestAbbrev As String Dim strTestName As String
LoadStateData()
Console.Write("Enter a state abbreviation (or just press Enter to quit): ") strTestAbbrev = UCase(Console.ReadLine())
Do Until strTestAbbrev = "" strTestName = GetStateName(strTestAbbrev)
If strTestName = "" Then Console.WriteLine("No state name found for '" & strTestAbbrev & "'.") Else Console.WriteLine("'" & strTestAbbrev & "' is the abbreviation for '" _ & strTestName & "'.") End If Console.WriteLine() Console.Write("Enter a state abbreviation (or just press Enter to quit): ") strTestAbbrev = UCase(Console.ReadLine()) Loop
End Sub
Private Sub LoadStateData()
Dim intStateFileNbr As Integer Dim intStateUB As Integer
intStateFileNbr = FreeFile() intStateUB = -1
FileOpen(intStateFileNbr, _ My.Application.Info.DirectoryPath & "\STATES.DAT", _ OpenMode.Input)
Do Until EOF(intStateFileNbr) intStateUB += 1 ReDim Preserve maudtStateRecord(intStateUB) With maudtStateRecord(intStateUB) Input(intStateFileNbr, .StateAbbrev) Input(intStateFileNbr, .StateName) End With Loop
FileClose(intStateFileNbr)
End Sub
Private Function GetStateName(ByRef pstrTestAbbrev As String) As String
Dim intX As Integer
For intX = 0 To UBound(maudtStateRecord) If pstrTestAbbrev = maudtStateRecord(intX).StateAbbrev Then Return maudtStateRecord(intX).StateName End If Next
' if we get here, the state was not found ... Return ""
End Function
End Module |
|
The technique used here is called a serial search, because the StateAbbrev elements of the maudtStateRecord structure array are compared one by one to the state abbreviation being looked for (pstrTestAbbrev) until either a match is found or all elements of the array are examined without finding a match. If a match on the state abbreviation is found, the corresponding state name is returned.
Download the VB project code for the example above here.
Binary Search Examples
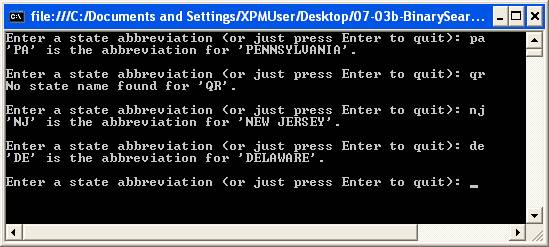
The serial search is fine for small or unsorted arrays, but for larger arrays, serial searching is inefficient. If an array is sorted (and that is important – in the case of the state data file we are working with, the records are sorted by state abbreviation, which is desirable), the very efficient technique of binary searching can be used. In a binary search, the element at the middle of the array is checked first. If a match is found, the search ends. Otherwise, the program determines whether the array argument needed is in the upper half of the array or the lower half. The half of the array containing the array argument is again halved and the search continues as before. The term "binary" here refers to this process of dividing by two.
The basic algorithm for a binary search is shown (in pseudocode) below:
Set MIN_INDEX = LBound(Array)
Set MAX_INDEX = UBound(Array)
Do While MIN_INDEX <= MAX_INDEX
Set MIDDLE_INDEX = INT((MIN_INDEX + MAX_INDEX) / 2)
If SEARCH_ITEM < ARRAY_ITEM(MIDDLE_INDEX) Then
Set MAX_INDEX = MIDDLE_INDEX – 1
ElseIf SEARCH_ITEM > ARRAY_ITEM(MIDDLE_INDEX) Then
Set MIN_INDEX = MIDDLE_INDEX + 1
Else
' Item has been found at MIDDLE_INDEX of array
Exit Do
End If
Loop
Binary Search Example 1
In the next programming example, the state lookup process has been modified to implement the binary search:
|
VB Code: |
Screen-shot of run: |
|
Module Module1
Private Structure StateRecord Dim StateAbbrev As String Dim StateName As String End Structure
Private maudtStateRecord() As StateRecord
Public Sub Main()
Dim strTestAbbrev As String Dim strTestName As String
LoadStateData()
Console.Write("Enter a state abbreviation (or just press Enter to quit): ") strTestAbbrev = UCase(Console.ReadLine())
Do Until strTestAbbrev = "" strTestName = GetStateName(strTestAbbrev)
If strTestName = "" Then Console.WriteLine("No state name found for '" & strTestAbbrev & "'.") Else Console.WriteLine("'" & strTestAbbrev & "' is the abbreviation for '" _ & strTestName & "'.") End If Console.WriteLine() Console.Write("Enter a state abbreviation (or just press Enter to quit): ") strTestAbbrev = UCase(Console.ReadLine()) Loop
End Sub
Private Sub LoadStateData()
Dim intStateFileNbr As Integer Dim intStateUB As Integer
intStateFileNbr = FreeFile() intStateUB = -1
FileOpen(intStateFileNbr, _ My.Application.Info.DirectoryPath & "\STATES.DAT", _ OpenMode.Input)
Do Until EOF(intStateFileNbr) intStateUB += 1 ReDim Preserve maudtStateRecord(intStateUB) With maudtStateRecord(intStateUB) Input(intStateFileNbr, .StateAbbrev) Input(intStateFileNbr, .StateName) End With Loop
FileClose(intStateFileNbr)
End Sub
Private Function GetStateName(ByVal pstrTestAbbrev As String) As String
Dim intMinIndex As Integer Dim intMaxIndex As Integer Dim intMidIndex As Integer
intMinIndex = 0 intMaxIndex = UBound(maudtStateRecord)
Do While intMinIndex <= intMaxIndex intMidIndex = Int((intMinIndex + intMaxIndex) / 2) If pstrTestAbbrev < maudtStateRecord(intMidIndex).StateAbbrev Then intMaxIndex = intMidIndex - 1 ElseIf pstrTestAbbrev > maudtStateRecord(intMidIndex).StateAbbrev Then intMinIndex = intMidIndex + 1 Else ' we have a match Return maudtStateRecord(intMidIndex).StateName End If Loop
' if we get here, the state was not found ... Return ""
End Function
End Module |
|
Download the VB project code for the example above here.
Binary Search Example 2
VB.Net introduced a number of methods that operate on arrays, one being BinarySearch, which implements the algorithm discussed above. The BinarySearch method operates on a one-dimensional array. The general syntax is:
Position = Array.BinarySearch(Array, ValueToFind)
where Array is the one-dimensional array to search, ValueToFind is the value that you are looking for, and Position is the index in the array where the item was found. If the item is not found, the value of Position will be a negative number.
Say we had an array of names as follows (note that the names are sorted):
Dim astrNames() As String = {"Archie", "Betty", "Charlie", "David", "Esther", "Frank", "George", "Heather", "Imogene", "Jack"}
Assuming you had a variable called intPosX defined As Integer, the following statements would produce the following results:
intPosX = Array.BinarySearch(astrNames, "Heather") ' intPosX would be 7
intPosX = Array.BinarySearch(astrNames, "Archie") ' intPosX would be 0
intPosX = Array.BinarySearch(astrNames, "Betty") ' intPosX would be 1
intPosX = Array.BinarySearch(astrNames, "Archie") ' intPosX would be a negative number, indicating the name was not found
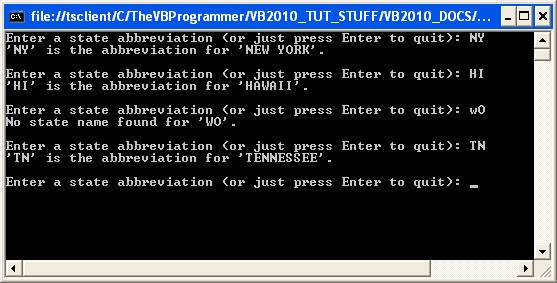
To use the BinarySearch method in our state name lookup example, we would need to modify the way we are storing the state abbreviations and their corresponding state names – because the BinarySearch method operates on a one-dimensional array, not a structure. A way to do it would be to store the data into two separate arrays: one for the state abbreviations, the other for the state names. The BinarySearch would operate on the state abbreviation array, and the resulting index for the found abbreviation would also be the index for the corresponding state name in the state name array. The example below demonstrates this:
|
VB Code: |
Screen-shot of run: |
|
Module Module1
Private mastrStateAbbrev() As String Private mastrStateName() As String
Public Sub Main()
Dim strTestAbbrev As String Dim strTestName As String
LoadStateData()
Console.Write("Enter a state abbreviation (or just press Enter to quit): ") strTestAbbrev = UCase(Console.ReadLine())
Do Until strTestAbbrev = "" strTestName = GetStateName(strTestAbbrev)
If strTestName = "" Then Console.WriteLine("No state name found for '" & strTestAbbrev & "'.") Else Console.WriteLine("'" & strTestAbbrev & "' is the abbreviation for '" _ & strTestName & "'.") End If Console.WriteLine() Console.Write("Enter a state abbreviation (or just press Enter to quit): ") strTestAbbrev = UCase(Console.ReadLine()) Loop
End Sub
Private Sub LoadStateData()
Dim intStateFileNbr As Integer Dim intStateUB As Integer
intStateFileNbr = FreeFile() intStateUB = -1
FileOpen(intStateFileNbr, _ My.Application.Info.DirectoryPath & "\STATES.DAT", _ OpenMode.Input)
Do Until EOF(intStateFileNbr) intStateUB += 1 ReDim Preserve mastrStateAbbrev(intStateUB) ReDim Preserve mastrStateName(intStateUB) Input(intStateFileNbr, mastrStateAbbrev(intStateUB)) Input(intStateFileNbr, mastrStateName(intStateUB)) Loop
FileClose(intStateFileNbr)
End Sub
Private Function GetStateName(ByVal pstrTestAbbrev As String) As String
Dim intPosition As Integer
intPosition = Array.BinarySearch(mastrStateAbbrev, pstrTestAbbrev)
If intPosition < 0 Then Return "" Else Return mastrStateName(intPosition) End If
End Function
End Module |
|
Download the VB project code for the example above here.